"Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things"
WEATHER AND CLIMATE
I have been teaching a variety of courses in geomatics, GIS, and climate. Below are links to the topics on weather and climate. These materials are also available at the University of Memphis eCourseware system.
To know more about each topic and picture, simply click on it!
Climate Controls, Variability and Change
In this lab you will analyze climate variability and change that can occur at a variety of different time scales.
Climate Classification
In this lab you will use monthly average temperature and precipitation data to identify the climate type or climate sub-type of a particular station. You will also use climate data to construct your own climograph.
Air Pollution
This lab focuses on air pollution. Through this exercise you will explore patterns in pollution concentrations as well as weather conditions that contribute to poor air quality near the Earth’s surface.
Hurricanes
This lab focuses on tropical systems. This lab exercise supports building your understanding of the tropical systems including: ingredients for formation, development, and impacts.
Midlatitude Cyclones and Thunderstorms
This lab concentrates on identifying fronts, air masses, understanding the structure of midlatitude cyclones, and the basics on tornadoes and the typical weather ingredients necessary for large outbreaks of tornadoes.
Atmospheric Motion
This lab concentrates on understanding the motion of air around high and low pressure centers and identifying these systems and the jet stream on weather maps.
Stability
This lab exercise will introduce you to atmospheric stability. You will see how air parcels behave as they move vertically in the atmosphere. You will also be introduced to a couple of key stability indices used in severe thunderstorm forecasting.
Atmospheric Moisture
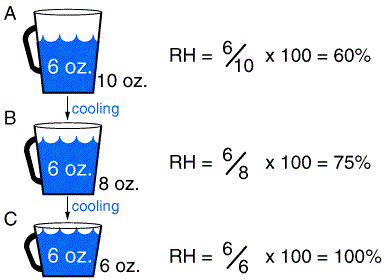
This lab will give you hands-on experience collecting data that can be used to determine two key moisture variables that are often used by meteorologists and climatologists—the relative humidity and the dew point. By the end of the lab, you should be familiar with how to use a sling psychrometer to determine the relative humidity and the dew point, the relationship between relative humidity and dew point, and the heat exchanges taking place as water changes phase.
Energy and Temperature
The temperature of the planet at any given time is a dependent upon the amount of sunlight that is received. This lab will stress key topics on energy and temperature from chapters 3 and 4 in the textbook, but you will also need to refer back to temperature scales in chapter 2 (page 46).
Introduction to Weather Data
This lab exercise will introduce you to universal time used in meteorology and how to convert that time to the more familiar time zones. You will see universal time used throughout the course. This lab exercise will also take a brief look at the vertical structure of the atmosphere and introduce you to some basics about weather maps.
* Exercises are provided by The Department of Earth Sciences, The University of Memphis, USA.